U.S. cancer deaths fall overall while colorectal cancer rises among adults under 50 and third trimester wildfire smoke exposure links to higher autism risk. The new data matter now because the cancer trend accelerates faster than predicted through 2023 and climate driven wildfires are increasing exposure across regions. Short term this raises screening and maternal health urgency in the United States and Western wildfire zones. Long term it may alter prevention priorities, research funding, and product demand in Europe, Asia, and emerging markets. Compared with the early 1990s, colorectal mortality climbed to first place for younger adults sooner than forecasts expected. Policymakers and health systems face both immediate and lasting implications.
Colorectal cancer climbs while overall cancer deaths decline
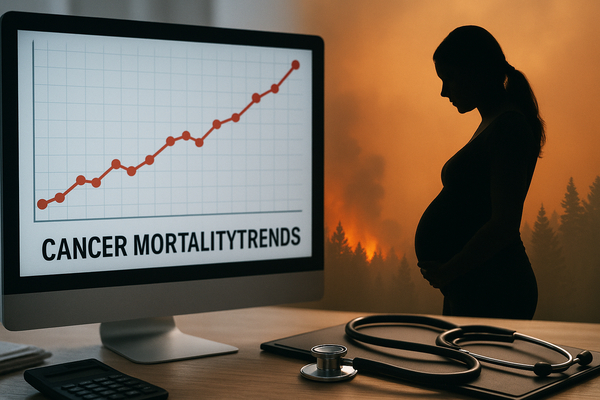
Cancer deaths among U.S. adults under age 50 declined for most leading malignancies between 1990 and 2023. However colorectal cancer moved opposite to that trend. Analysis published in JAMA shows nearly 1.3 million U.S. deaths from cancer before age 50 from 1990 through 2023. The age adjusted cancer death rate fell 44 percent from 25.5 to 14.2 per 100,000 adults over that period.
Yet colorectal cancer mortality rose by an average 1.1 percent each year from 2005 through 2023. That gain pushed colorectal cancer from fifth place in the early 1990s to the leading cause of cancer death in the under 50 group earlier than researchers expected. The American Cancer Society led the analysis and urged greater public education about warning signs such as bright red blood in stool and persistent abdominal pain. Researchers also recommended screening start at age 45 for higher detection of earlier stage disease.
Clinically and commercially there are knock on effects. Screening technologies and diagnostic services draw more attention and investment. An example is Abbott (NYSE:ABT) pursuing larger roles in cancer screening through its planned deal for Exact Sciences (NASDAQ:EXAS). Regulators and payers will evaluate guideline changes. Hospitals and oncologists must prepare for more younger patients with advanced disease. Meanwhile drug approvals and partnerships will also shape treatment availability. For instance Amgen (NASDAQ:AMGN) recently received U.S. approval for a colorectal cancer therapy, and global licensing deals are expanding development pipelines.
Third trimester wildfire smoke exposure tied to higher autism diagnoses
A California study of over 200,000 births in Southern California between 2006 and 2014 found a statistical association between maternal exposure to wildfire smoke in the third trimester and higher risk of autism diagnoses by age five. The cohort included 3,356 children diagnosed with autism. Mothers exposed to one to five days of wildfire smoke particles in the final trimester had higher odds of an autism diagnosis in their child compared with mothers with no exposure. The strongest association occurred with more than 10 days of exposure, where the risk rose by 23 percent.
Researchers stressed the study does not prove causal connection. They noted that wildfires emit particulate matter, toxic metals, and other pollutants that can cross the maternal barrier or alter in utero development. Risk factors clustered with older maternal age, first pregnancies, and pre pregnancy conditions such as diabetes and obesity. The finding fits into a wider body of research linking air pollution to altered fetal brain development.
From a policy perspective the timing is urgent. Climate driven increases in fire frequency and intensity have raised exposure in the western United States, Mediterranean Europe, Australia, and parts of Asia and Latin America. Health systems must weigh short term public guidance on exposure reduction and long term investments in air quality monitoring and maternal care. The study adds data points that could influence maternal health advisories and environmental regulation.
Industry reaction and market implications for health companies
These clinical findings arrive while industry faces regulatory and reputational headwinds that affect investment, trials, and supply chains. Sweeping policy moves under the U.S. Health Secretary have had a chilling effect on vaccine makers, according to executives and investors. Moderna (NASDAQ:MRNA) has curtailed some vaccine trial investments after heightened scrutiny. Novavax (NASDAQ:NVAX) and Pfizer (NYSE:PFE) signed a licensing agreement to coordinate vaccine development, and Merck (NYSE:MRK) partnered with a global health coalition to advance an affordable Ebola vaccine.
Product safety issues and recalls are also reshaping markets. Major infant formula manufacturers scrambled after contamination concerns. Danone (EPA:BN) saw shares slide when a regulator asked it to block a batch. Lactalis issued recalls for baby milk batches. These events affect supply chains and consumer trust and can influence short term revenue and longer term brand strategies.
At the corporate earnings level some companies reported mixed results. Abbott lowered near term profit guidance tied to portfolio moves. Johnson & Johnson (NYSE:JNJ) projected profit for 2026 above Wall Street estimates. Dr Reddy’s (NYSE:RDY) reported smaller than expected quarterly profit. UnitedHealth (NYSE:UNH) announced plans to offer rebates to Obamacare customers. Biotech collaborations continue. Janux Therapeutics paired with Bristol Myers (NYSE:BMY) on a potential $850 million oncology deal. Corcept (NASDAQ:CORT) reported clinical data showing its cancer drug reduced risk of death in an ovarian cancer trial.
The near term market response includes increased volatility in health stocks, potential reallocation of R&D budgets, and selective consolidation. Investors and management teams may further prioritize diagnostics and therapies that address rising colorectal incidence and maternal environmental risks. In addition public health policy and regulatory attention are likely to alter trial design, labeling and communication strategies.
What this means for regions and stakeholders
In the United States the dual signals of a rising cancer burden in younger adults and environmental risks for prenatal development create immediate priorities for screening, maternal health, and air quality mitigation. In Europe and Asia regulators and health systems will monitor data and may adapt screening age recommendations and environmental guidance. Emerging markets face a mixed picture. Some will see growing demand for diagnostics and maternal care as urbanization and pollution change exposure patterns. Others will confront access challenges where screening and specialist care are limited.
Data through 2023 and the wildfire study together point to linked health and environmental drivers. Policymakers, health systems, and market participants will need to coordinate clinical guidance, surveillance, and product development. Meanwhile companies in diagnostics, therapeutics, and public health services are adjusting strategies in response to regulatory scrutiny, recalls, and changing demand.
This report is for informational use only. It does not provide financial or medical advice.












